If you’ve been doing your own research on Bitcoin (BTC), you might have come across the term “hash rate.” It’s more commonly used when discussing Bitcoin mining, but has become a need-to-know metric for many involved in the market.
Defining the hash rate and how it works
A hash is data encrypted with a 64-digit hexadecimal number. For every transaction in the Bitcoin blockchain, the network randomly assigns it a unique hash that may look something like:
000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
This unique hash, also called a target hash, needs to be validated and added to the public ledger by other network participants. Decrypting and validating hashes is resource intensive and that’s why the network participants are rewarded with Bitcoin if they are the first to complete the process. This process of decrypting and validating unique hashes is also called “Bitcoin mining.”
Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin mining doesn’t involve complex computations. What Bitcoin miners actually do is try to be the first to “guess” the correct target hash. As you can imagine, the possible combinations are almost unlimited since the target hash is composed of 64 digits and is randomly generated. It would take a long time for a laptop or regular desktop computer to arrive at the correct target hash.
To speed up the mining process, miners use powerful computers to brute force every possible combination. These mining rigs can try 1 billion hash combinations per second (gigahash/second) up to hundreds of trillions per second (terahash/second). “Hash rate” is the number of hashes produced per second and is used to measure the computing power of mining rigs.
Hash rate also refers to the combined computing power of all network participants in the Bitcoin blockchain. A high hash rate means that more machines are willing to validate Bitcoin transactions and vice versa.
What makes a good hash rate?
With all the technical details out of the way, let’s answer the question: “what makes a good hash rate?” Generally speaking, a high hash rate is preferred by miners as this increases the security and capacity of the network.
Let’s talk about the first bit, security. A higher hash rate means that more miners are able to help verify transactions, meaning that the network’s security is in a healthy state.
A high hash rate also means that miners are capable of processing more transactions at a faster rate. This increase in the capacity of the network makes it more efficient since more people can use the network for their transactions.
Hash rate measurements and units
When computing hash rates, the unit h/s (hashes per second) is used. This is used to gauge the speed of the machine used for Bitcoin mining. Metric terms like kilo, mega, giga, tera, peta, and exa are used to distinguish the degree of the hash rate.
1 kilo hash per second (1 Kh/s) = one thousand hashes per second (1,000 h/s)
1 mega hash per second (1 Mh/s) = one million hashes per second (1,000,000 h/s)
1 giga hash per second (1 Gh/s) = one billion hashes per second (1,000,000,000 h/s)
1 tera hash per second (1 Th/s) = one trillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000 h/s)
1 peta hash per second (1 Ph/s) = one quadrillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000,000 h/s)
1 exa hash per second (1 Eh/s) = one quintillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000,000,000 h/s)
One thing to note is that hash rates vary depending on the cryptocurrency and what machine or equipment was used to mine it. Different cryptocurrencies don’t have the same amount of hash power.
Hash rates over time
A better way to understand all this is by taking a look at the history of Bitcoin’s hash rate. Below, you’ll find a chart showing us Bitcoin’s hash rate and value over the past three years:
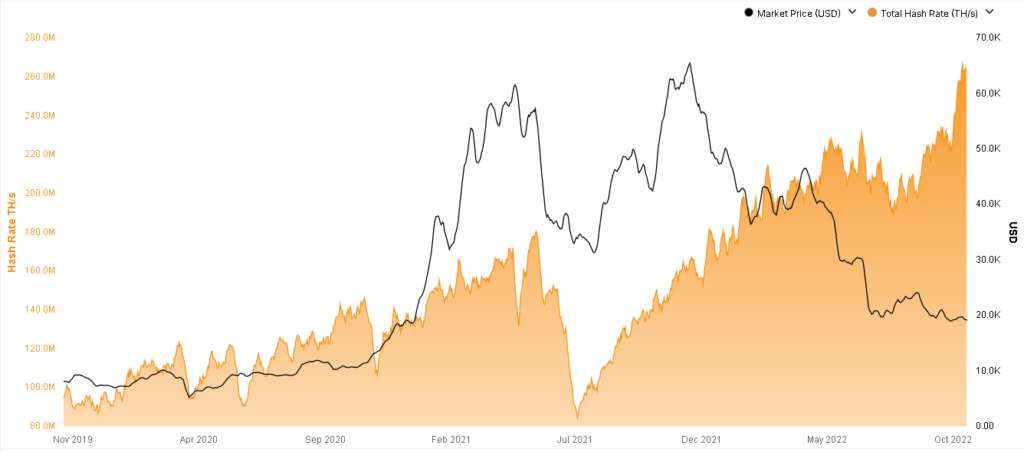
Retrieved from: https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/charts/hash-rate on October 18, 2022.
There’s a lot to digest here, so let’s look at it step-by-step. Let’s start with Bitcoin’s earlier years, before the influx of traders and investors. The chart starts sometime around November 2019 and shows that Bitcoin’s value was hovering around the 10,000 USD mark, and the hash rate was just above 100 million TH/s.
Over the next few months, we would see a simultaneous increase in both metrics as Bitcoin’s value would skyrocket to just above 61,000 USD. At the time, the hash rate would be a little over 150 million TH/s. While relatively proportional at first, Bitcoin’s growth would eventually far outpace its hash rate.
We see a similar trend when Bitcoin hit its all-time high of 65,496 USD in December 2021. That peak would coincide with the Bitcoin hash rate’s recovery from an earlier slump.
An all-time high
On October 17, 2022, Bitcoin’s hash rate reached an all-time high, hitting a little over 265 million TH/s. While this does come at a time when Bitcoin’s value is still suffering from the effects of crypto winter, it’s seen as a sign that this winter just might be ending.
Impact of the hash rates on the Bitcoin network
Hash rates directly affect cryptocurrency miners, whether they are mining on their own or via mining pools. That won’t be their only effect, though, as we’ll soon see:
Bitcoin’s relationship with hash rates
Over its history, Bitcoin’s hash rate has developed into a leading indicator of Bitcoin’s price—an upswing in hash rate then implies that Bitcoin’s value would see similar improvements.
This relationship has held true for the most part, the only difference being the crypto winter we are experiencing in 2022. That said, the hash rate’s credibility as a leading indicator has not been affected. This is because the hash rate signals miners’ intentions. With more miners, confidence in the network increases as well.
A potential signal for bullish behavior
As we mentioned earlier, Bitcoin’s hash rate shows some parallel with Bitcoin’s value. After all, an increase in Bitcoin’s hash rate is an increase in the network’s efficiency and security.
This has led many to believe that the fact we’ve hit a hash rate all-time high means we should expect early signs of bullish behavior. This should be positive news for many of us who’ve been waiting for the end of the bear market.
Effects on energy consumption
Since hash power also relies on the performance of the computers used in mining, a lot of miners are investing in powerful equipment to have more chances of having higher hash rates. These computers are expensive and consume large amounts of electricity to run their operations.
Before, miners could acquire cryptocurrencies using ordinary computers and graphic cards. However, with the rising popularity of Bitcoin and other digital currencies, a lot of miners have joined the competition with new and more powerful mining hardware like the application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miners.
These factors caused the Bitcoin hash rate to increase immediately and eventually paved the way for the mining difficulty level to rise. As the mining difficulty increases, more energy is consumed by computers.
The importance of hash rates
As we learn more about Bitcoin’s hash rate, we can see how it can be an important measurement—particularly for miners. To them, it’s a sign of greater competition since there would be other miners to compete with in the race to get the right block hash.
For the average consumer, it’s a sign of Bitcoin miners’ intent. Higher hash rates imply that more miners are present, using capable machines to boost their hash power. If miners are willing to invest money into mining Bitcoin, the consumer’s confidence in the network will grow as well.
For investors, the same sentiment will hold. Greater confidence in Bitcoin’s network means that more investors can feel safe with their investments thanks to the greater security that high hash rates promise. This could potentially boost the value of Bitcoin as more and more investors choose to put their money into the network.
The sum of it is that Bitcoin’s hash rate is a good signal of the health of the network. It may not be definitive, but it’s a good metric to keep an eye on for anyone involved in the network. Use it as a guide for your trades or as a general “thermometer” of the market’s current capacity—the important thing is to remember to use all the tools available to you.